Readme
Stable Diffusion is a latent text-to-image diffusion model capable of generating photo-realistic images given any text input.
We’ve generated updated our fast version of Stable Diffusion to generate dynamically sized images up to 1024x1024. Here’s links to the current version for 2.1 and 1.5:
| Stable Diffusion Version | Optimized for speed, flexible image sizes |
|---|---|
| 2.1 | link |
| 1.5 | link |
All previous versions of Stable Diffusion will continue to be on Replicate, see the version list for further details: https://replicate.com/stability-ai/stable-diffusion/versions
- Developed by: Robin Rombach, Patrick Esser
- Model type: Diffusion-based text-to-image generation model
- Language(s): English
- License: The CreativeML OpenRAIL M license is an Open RAIL M license, adapted from the work that BigScience and the RAIL Initiative are jointly carrying in the area of responsible AI licensing. See also the article about the BLOOM Open RAIL license on which our license is based.
- Model Description: This is a model that can be used to generate and modify images based on text prompts. It is a Latent Diffusion Model that uses a fixed, pretrained text encoder (CLIP ViT-L/14) as suggested in the Imagen paper.
- Resources for more information: GitHub Repository, Paper.
- Cite as:
@InProceedings{Rombach_2022_CVPR,
author = {Rombach, Robin and Blattmann, Andreas and Lorenz, Dominik and Esser, Patrick and Ommer, Bj\"orn},
title = {High-Resolution Image Synthesis With Latent Diffusion Models},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)},
month = {June},
year = {2022},
pages = {10684-10695}
}
Uses
Direct Use
The model is intended for research purposes only. Possible research areas and tasks include
- Safe deployment of models which have the potential to generate harmful content.
- Probing and understanding the limitations and biases of generative models.
- Generation of artworks and use in design and other artistic processes.
- Applications in educational or creative tools.
- Research on generative models.
Excluded uses are described below.
Misuse, Malicious Use, and Out-of-Scope Use
Note: This section is taken from the DALLE-MINI model card, but applies in the same way to Stable Diffusion v1.
The model should not be used to intentionally create or disseminate images that create hostile or alienating environments for people. This includes generating images that people would foreseeably find disturbing, distressing, or offensive; or content that propagates historical or current stereotypes.
Out-of-Scope Use
The model was not trained to be factual or true representations of people or events, and therefore using the model to generate such content is out-of-scope for the abilities of this model.
Misuse and Malicious Use
Using the model to generate content that is cruel to individuals is a misuse of this model. This includes, but is not limited to:
- Generating demeaning, dehumanizing, or otherwise harmful representations of people or their environments, cultures, religions, etc.
- Intentionally promoting or propagating discriminatory content or harmful stereotypes.
- Impersonating individuals without their consent.
- Sexual content without consent of the people who might see it.
- Mis- and disinformation
- Representations of egregious violence and gore
- Sharing of copyrighted or licensed material in violation of its terms of use.
- Sharing content that is an alteration of copyrighted or licensed material in violation of its terms of use.
Limitations and Bias
Limitations
- The model does not achieve perfect photorealism
- The model cannot render legible text
- The model does not perform well on more difficult tasks which involve compositionality, such as rendering an image corresponding to “A red cube on top of a blue sphere”
- Faces and people in general may not be generated properly.
- The model was trained mainly with English captions and will not work as well in other languages.
- The autoencoding part of the model is lossy
- The model was trained on a large-scale dataset LAION-5B which contains adult material and is not fit for product use without additional safety mechanisms and considerations.
- No additional measures were used to deduplicate the dataset. As a result, we observe some degree of memorization for images that are duplicated in the training data. The training data can be searched at https://rom1504.github.io/clip-retrieval/ to possibly assist in the detection of memorized images.
Bias
While the capabilities of image generation models are impressive, they can also reinforce or exacerbate social biases. Stable Diffusion v1 was trained on subsets of LAION-2B(en), which consists of images that are primarily limited to English descriptions. Texts and images from communities and cultures that use other languages are likely to be insufficiently accounted for. This affects the overall output of the model, as white and western cultures are often set as the default. Further, the ability of the model to generate content with non-English prompts is significantly worse than with English-language prompts.
Training
Training Data The model developers used the following dataset for training the model:
- LAION-2B (en) and subsets thereof (see next section)
Training Procedure Stable Diffusion v1 is a latent diffusion model which combines an autoencoder with a diffusion model that is trained in the latent space of the autoencoder. During training,
- Images are encoded through an encoder, which turns images into latent representations. The autoencoder uses a relative downsampling factor of 8 and maps images of shape H x W x 3 to latents of shape H/f x W/f x 4
- Text prompts are encoded through a ViT-L/14 text-encoder.
- The non-pooled output of the text encoder is fed into the UNet backbone of the latent diffusion model via cross-attention.
- The loss is a reconstruction objective between the noise that was added to the latent and the prediction made by the UNet.
We currently provide three checkpoints, sd-v1-1.ckpt, sd-v1-2.ckpt and sd-v1-3.ckpt,
which were trained as follows,
sd-v1-1.ckpt: 237k steps at resolution256x256on laion2B-en. 194k steps at resolution512x512on laion-high-resolution (170M examples from LAION-5B with resolution>= 1024x1024).sd-v1-2.ckpt: Resumed fromsd-v1-1.ckpt. 515k steps at resolution512x512on “laion-improved-aesthetics” (a subset of laion2B-en, filtered to images with an original size>= 512x512, estimated aesthetics score> 5.0, and an estimated watermark probability< 0.5. The watermark estimate is from the LAION-5B metadata, the aesthetics score is estimated using an improved aesthetics estimator).-
sd-v1-3.ckpt: Resumed fromsd-v1-2.ckpt. 195k steps at resolution512x512on “laion-improved-aesthetics” and 10\% dropping of the text-conditioning to improve classifier-free guidance sampling. -
Hardware: 32 x 8 x A100 GPUs
- Optimizer: AdamW
- Gradient Accumulations: 2
- Batch: 32 x 8 x 2 x 4 = 2048
- Learning rate: warmup to 0.0001 for 10,000 steps and then kept constant
Evaluation Results
Evaluations with different classifier-free guidance scales (1.5, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, 6.0, 7.0, 8.0) and 50 PLMS sampling steps show the relative improvements of the checkpoints:
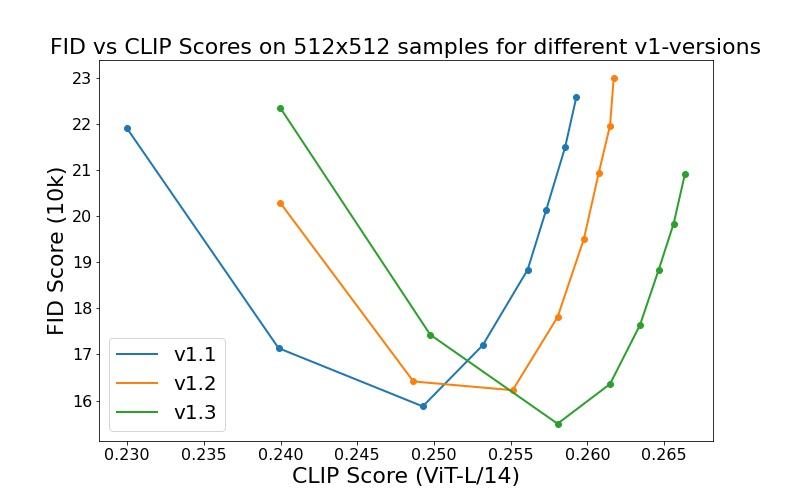
Evaluated using 50 PLMS steps and 10000 random prompts from the COCO2017 validation set, evaluated at 512x512 resolution. Not optimized for FID scores.
Environmental Impact
Stable Diffusion v1 Estimated Emissions Based on that information, we estimate the following CO2 emissions using the Machine Learning Impact calculator presented in Lacoste et al. (2019). The hardware, runtime, cloud provider, and compute region were utilized to estimate the carbon impact.
- Hardware Type: A100 PCIe 40GB
- Hours used: 150000
- Cloud Provider: AWS
- Compute Region: US-east
- Carbon Emitted (Power consumption x Time x Carbon produced based on location of power grid): 11250 kg CO2 eq.
Citation
@InProceedings{Rombach_2022_CVPR,
author = {Rombach, Robin and Blattmann, Andreas and Lorenz, Dominik and Esser, Patrick and Ommer, Bj\"orn},
title = {High-Resolution Image Synthesis With Latent Diffusion Models},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)},
month = {June},
year = {2022},
pages = {10684-10695}
}
This model card was written by: Robin Rombach and Patrick Esser and is based on the DALL-E Mini model card.